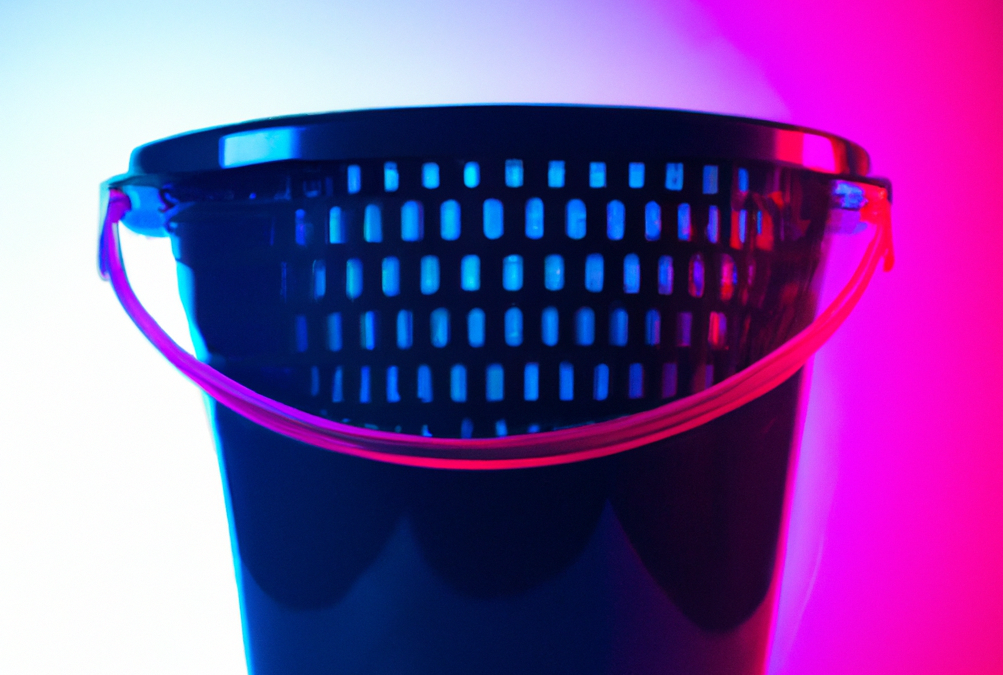
If you are thinking of manufacturing of a plastic bucket just be aware that it involves several steps in the injection molding process. These steps may vary depending on your personal preferences/ideas, but here’s a general overview of how manufacturing a plastic bucket can be done:
To make a plastic bucket you need to: have a 3d model of the bucket, have a mold designed based on your 3d model, have an injection molding machine set up and ready.
1. What material should I use to make a plastic bucket?
Before you choose the type of plastic material suitable for the bucket’s intended use, learn their properties. You can also visit your local supermarket and see yourself what materials are widely used in production. I will only tell you that the most common options include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
2. Do I need a mould to make a plastic bucket? How to go about the mould design?
Yes, you do! Easier said than done – Design a mold for the plastic bucket! The good thing is that the mold will have only two halves, one for the outer shape of the bucket, and one for the inner contours. So no side actions for mold undercuts. Did you consider a handle? It is going to be a separated part or integrated in to the design? It is worth mentioning that the mold should be made from durable materials like steel or aluminium.
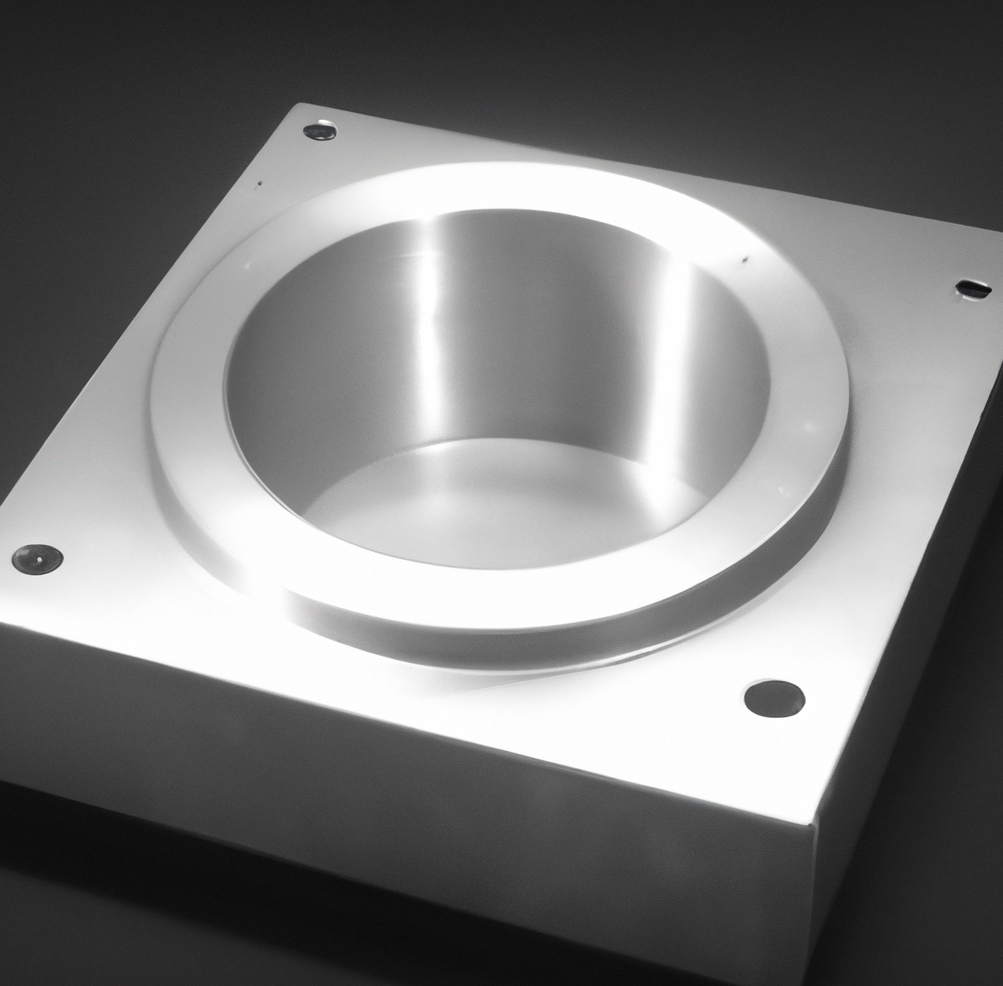
3. What happens to plastic material during making of a bucket?
The selected plastic material is melted and prepared for injection molding. This is typically done in a hopper, where the plastic pellets are fed into a heating chamber and melted to a specific temperature.
4. Is an Injection Molding a typical process for a plastic bucket manufacturing?
Yes, it is, alongside with a blow molding process. These two manufacturing methods are widely used in bucket making.
In case of injection molding the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. It fills the space inside the mold, taking the shape of the bucket. The plastic is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold.
In case of blow molding compressed air is injected into the parison, causing it to expand and take on the shape of the mold cavity. The air pressure forces molten, flexible plastic to conform to mold’s interior shape.
After injection, the mold is cooled to allow the plastic to harden and take the desired shape. Cooling may be done using water or air.
5. How hard is to open a plastic bucket mold after an injection molding?
Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the newly formed bucket should be easily ejected from the mold. Of course, I assume you didn’t forget about draft angles! To make the opening of your mold easier, you can build slots into your mold design. For smaller components you should be able to use a screwdriver to pop open the top half of your mold. Any possible flash of material also shouldn’t affect mold ejection. And if your airvents are done correct, and you applied hydraulic pressure to clamp both halves of your mold together, you shouldn’t have much problems with flash at all.
6. Do I need to trim or do any surface finish treatment to my own plastic bucket?
Yes, you do, although the better the surface of your mold cavity is, the less potential surface treatment you would have to perform to achieve desired surface finish. Any excess plastic or flash around the edges of the bucket should be trimmed and removed. The bucket may also undergo additional finishing processes, such as smoothing out rough edges or adding any necessary markings or labels.

7. What is quality control for my plastic injection molding bucket?
Your buckets should undergo quality control checks to ensure they meet the desired specifications. It is good to determine a sampling plan, as you won’t be able to check each and every bucket that leaves the production. For plastic, thin wall components such us buckets, surface finish and loose dimension tolerance control can be performed. This can include a visual inspection for deforms, material defects, dimensions, and overall quality.
For more technical objects, an inspection of critical dimensions, tolerances, material requirements, appearance criteria and any other relevant factors should be carried out.
The control should be determined during production, when the product pops out of the mold as well as during its functional utilisation.
It’s important to note that manufacturing plastic buckets requires specialized equipment and expertise. It’s not a simple DIY project but rather an industrial process that involves precision and safety measures. Additionally, specific techniques and machinery may vary depending on the scale of production and the specific design of the bucket. Manufacturers often have experienced engineers and technicians who oversee the entire process to ensure quality and consistency.