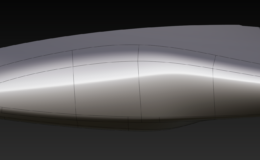
What is CAS (Computer-Aided Styling)?
CAS, or Computer-Aided Styling, is the digital design process used to craft and refine the visual aesthetics of a product, focusing on its form, surfaces, and overall appearance. 3D product modeling. Objects are created in 3D software using a combination of sketches, flat renderings, verbal descriptions, or even physical prototypes as references.
Why is CAS Essential in 3D Product Design?
CAS is crucial in 3D product design because it offers virtually unlimited possibilities for creating complex shapes and forms. Unlike other techniques, it allows designers to easily achieve visual harmony and balance, making it an essential tool for shaping products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. The only limitations are the skill and creativity of the user. Experienced 3D modelers can create products with striking visual appeal, and CAS has long been used in high-demand applications such as automotive A-Class surfacing. Today, it is gaining traction across various other industries, proving its versatility and importance in modern design of industrial digital product design.
3D Modeling – Theoretical Intersection and Patch Layout
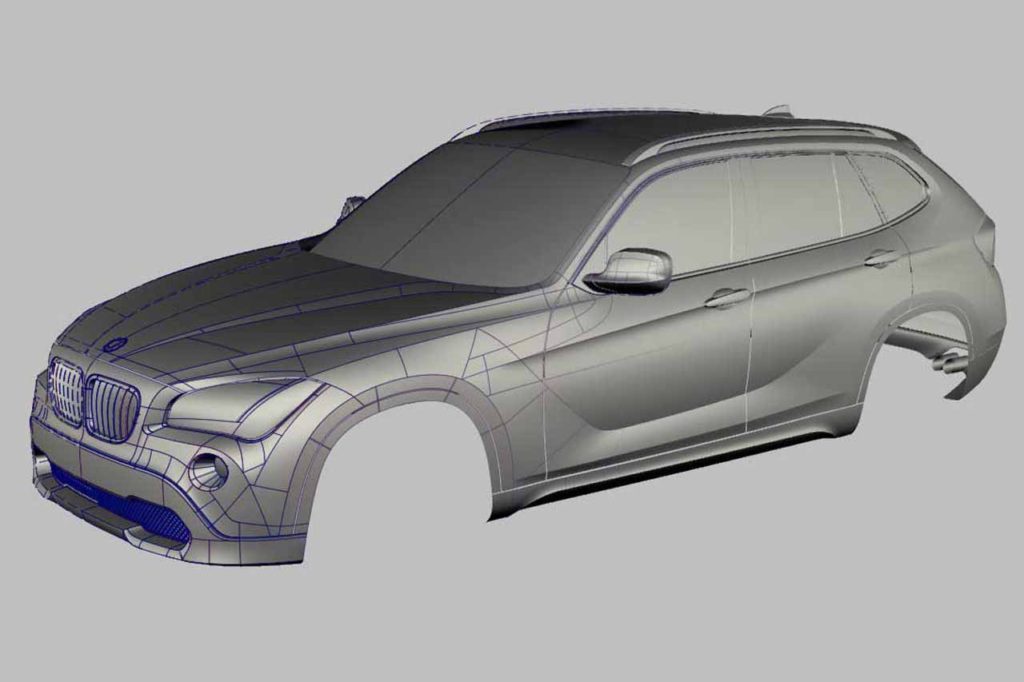

An efficient patch layout ensures seamless theoretical intersections, or ‘theories,’ between surfaces. The primary ‘slab’ geometry is generated within the designer’s defined boundary of curve networks. This topology is both simple and flexible, making it easy to modify and implement design changes as needed.
Autodesk Alias Geometrical Technicality
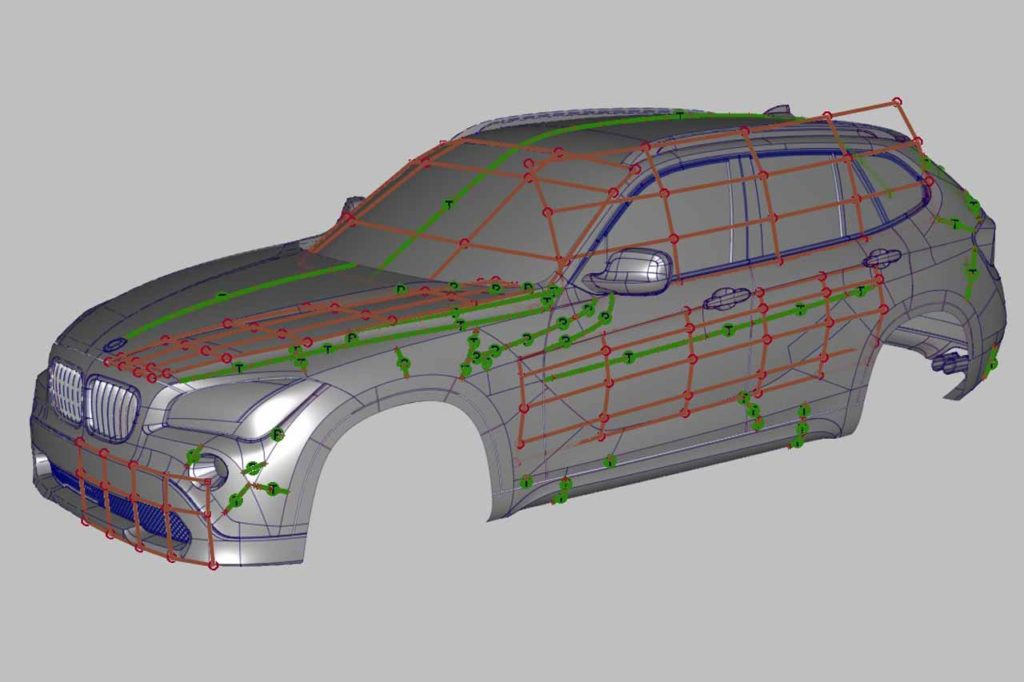
While CAS software may appear complex at first, it provides complete control over geometric precision. The topology can be modeled with an active construction history, allowing designers to track and modify changes as the design evolves, enabling 3D digital models to follow the designer’s manipulations and update accordingly. Models can be sculpted to the designer’s liking, with light-sensitive highlights polished to perfection and value-sensitive geometric forms sculpted.
Automotive Sculpting – Quality Evaluation

The comb curvature plot is the ultimate A-Class evaluation tool, capable of revealing surface flaws that Zebra Stripe analysis might overlook. Using the comb evaluation in the final stages of 3D CAS modeling complements Zebra Stripe analysis by effectively highlighting distortions, discontinuities, and tears, ensuring the surface is flawless.
Dicigal Sculpting – Beauty and Grace
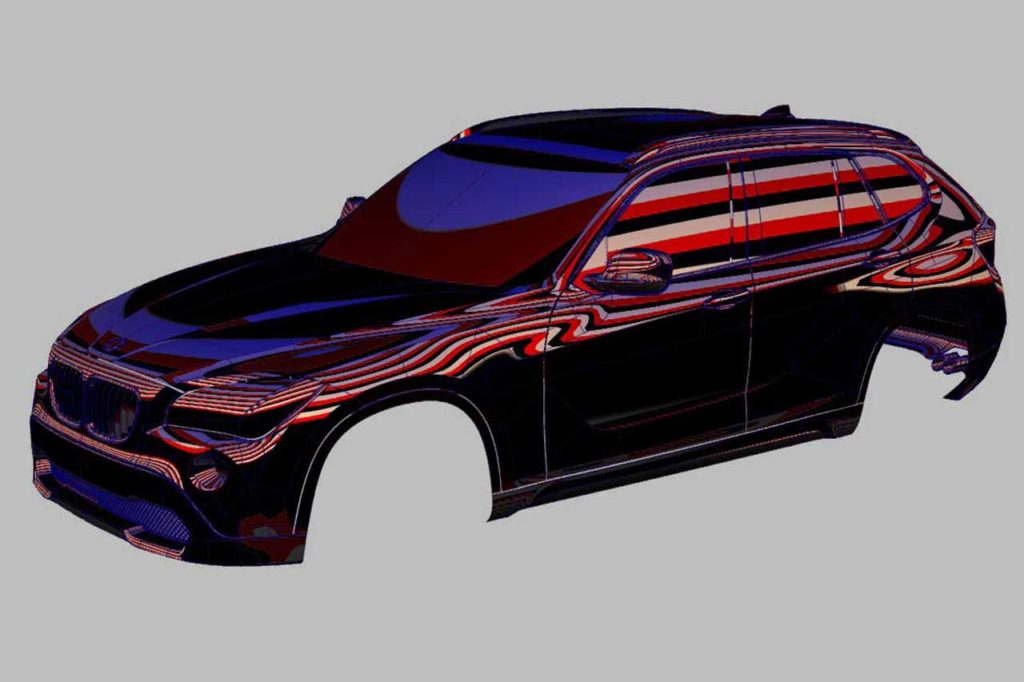
CAS modeling combines the precision of technical surfacing with the creativity of visual sculpting. 3D modelers can effortlessly switch between engineering and design roles. For instance, stripes applied to the topology can guide shape adjustments, with engineers using techniques like curve manipulation or surface modification to refine the design.
Super Real Rendering – Environmental Representation
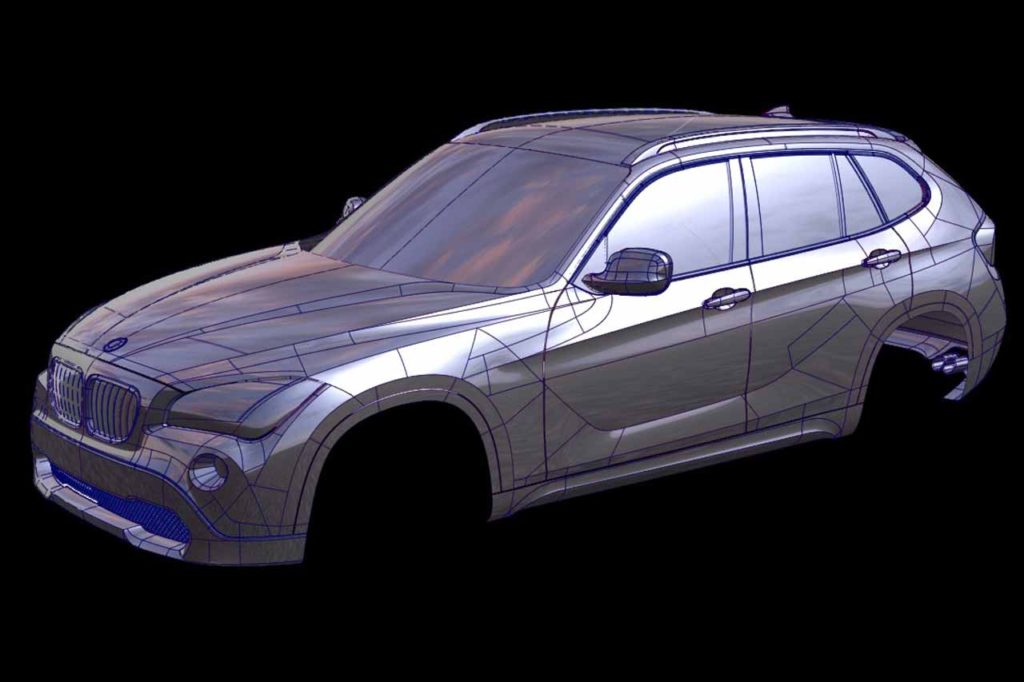

Viewing 3D CAS models in full environmental rendering is truly rewarding, offering a preview of the final product. While some areas may still require refinement, the model comes to life in both virtual and real-world contexts. At this stage, Zebra Highlights take a backseat as the model’s volumes and proportions become the focus. Ultimately, the tactile and visual experience of the design outweighs the need for perfect highlight scrutiny.
Show Must Go On
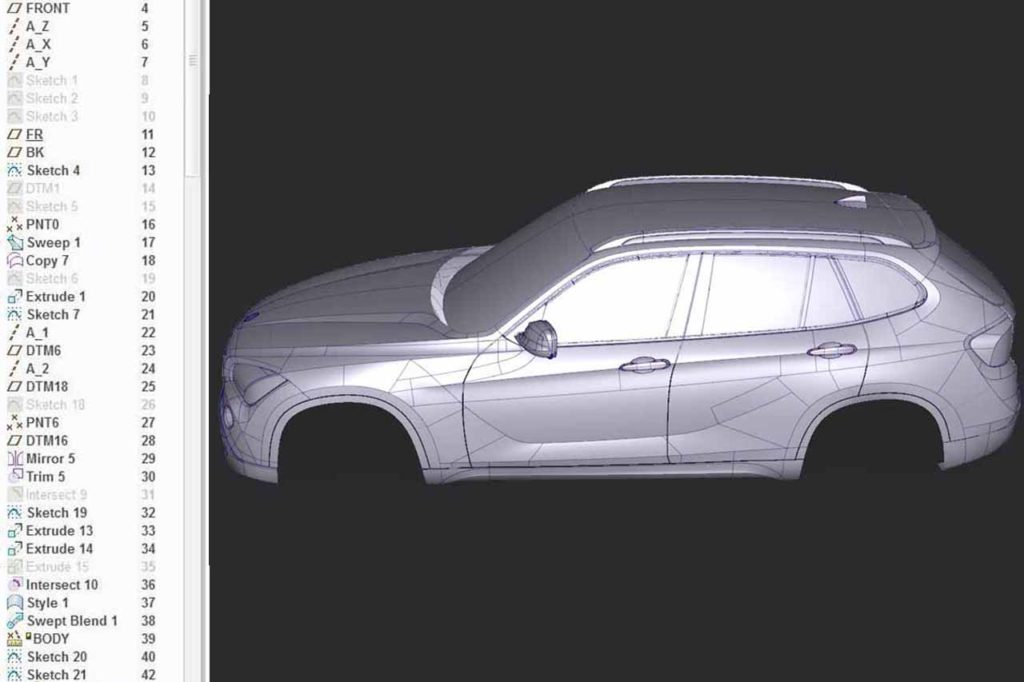

It’s time to hand over the 3D model, now refined into an A-Class ‘skin,’ to the engineering team. At this stage, the model is thickened, and smaller, simpler rounds and fillets are added. If transferring data between CAD systems causes any topology issues, the digital data may be sent back to the CAS modelers for refinement. Once everything is finalized, the skin surfaces are converted into a solid model, ready for tooling or rapid prototyping.
Conclusion
CAS modeling is a cornerstone of modern design studios. 3D digital styling is now widely used not only in automotive design but also across various industrial product design sectors, where the freedom and precision of Computer-Aided Styling are highly valued. Leading software tools in the industry include Alias Autodesk, ICEM Surf, and Catia V5. If you’re serious about creating competitive 3D digital models, consider one of these premier packages.